Introduction
Anesthesia has transformed modern medicine by allowing surgeries and procedures to be performed without pain or distress. But not all anesthesia is the same. In this blog, we’ll break down the four main types of anesthesia, how they work, and when each is used—explained in simple terms for everyone.
- General Anesthesia
Definition:
A controlled, unconscious state used during major surgeries like heart, brain, or abdominal procedures.

How It’s Given:
IV (intravenous) medications
Inhaled gases through a mask or breathing tube
What It Does:
You are fully asleep and unaware of anything
No memory or sensation of pain
Monitoring:
Doctors monitor heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen levels, and breathing continuously.
Common Side Effects:
Nausea and vomiting
Sore throat (due to breathing tube)
Drowsiness or grogginess
- Regional Anesthesia
Definition:
Blocks pain in a larger region of the body while you stay awake or lightly sedated.
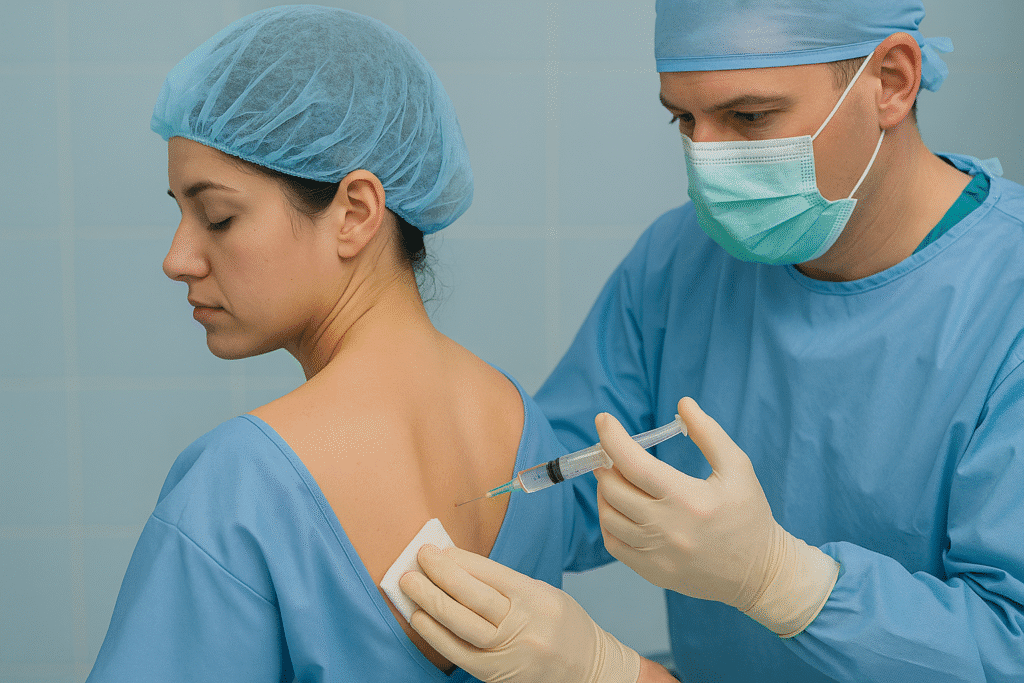
Common Types:
Spinal Anesthesia: Injected into spinal fluid; used for lower abdominal, pelvic, or leg procedures.
Epidural Anesthesia: Delivered through a catheter; popular during childbirth.
Nerve Blocks: Used for targeted numbness in limbs or specific body areas.
Advantages:
Safer option for certain patients
Fewer systemic effects than general anesthesia
Side Effects:
Low blood pressure
Headache (especially with spinal anesthesia)
Temporary numbness or weakness
- Local Anesthesia
Definition:
Numbs a small, specific area for minor procedures like dental work or mole removal.

How It’s Given:
Injected directly into the tissue where the procedure occurs.
Benefits:
Quick and effective
No loss of consciousness
Minimal side effects
Possible Reactions:
Mild burning sensation at the injection site
Rare allergic responses
- Sedation (Conscious Sedation or Monitored Anesthesia Care)
Definition:
Used to relax patients during less invasive procedures, often combined with local or regional anesthesia.

Sedation Levels:
Minimal: Calm but fully awake
Moderate: Drowsy, limited memory
Deep: Near unconsciousness but responsive to touch or voice
Common Uses:
Endoscopy
Colonoscopy
Some dental procedures
Side Effects:
Drowsiness
Brief confusion or slowed breathing (if deep sedation)
How Doctors Choose the Right Type
The choice depends on:
Type and duration of the procedure
Your health history
Preferences and risk factors
Anesthesiologist’s evaluation
Before surgery, your doctor will explain your anesthesia plan and answer any questions you have.
Conclusion
Anesthesia is a powerful tool that makes medical care safer, more comfortable, and nearly painless. Whether you’re undergoing a simple procedure or a complex surgery, understanding the type of anesthesia used can ease your anxiety and help you feel more informed.
Tip: Always discuss your concerns and medical history with your anesthesia provider beforehand.